The researchers first carried out epigenome-wide association for incident T2D using baseline samples collected at enrolment for 5,709 Asian individuals, from three prospective population-based cohorts. To further explore potential genetic and environmental factors influencing methylation, the researchers used data from an independent multi-ethnic Asian population cohort with deep clinical and molecular phenotyping. This was supplemented by functional genomic analyses and fine-mapping via targeted sequencing of selected top loci. The researchers then tested the potential utility of DNA methylation for prediction of T2D via a Methylation Risk Score (MRS) approach
DNA methylation array: DNA methylation was quantified in genomic DNA from whole blood, using the Illumina® EPIC or 450K array which covered 2-3% of the epigenome. This allowed the scientists to identify genomic loci that were associated with incident T2D.
Whole genome bisulfite sequencing (WGBS): DNA methylation across the entire epigenome was analyzed using libraries construction with the Accel-NGS® Methyl-Seq DNA Library Kit (Swift Biosciences), and sequenced on the Illumina® NovaSeq platform. WGBS made possible the identification of correlated regions in the epigenome, which further informs the design of the targeted methylation sequencing.
Targeted methylation sequencing: Fine-mapping of regions of interest were interrogated by using a custom array (TWIST Biosciences). The targeted methylation sequencing allowed the researchers to investigate these regions of interest in a high resolution fashion.
HPC resources used: This project was allocated 1,320,959 CPU hours on NSCC Singapore’s supercomputing resources
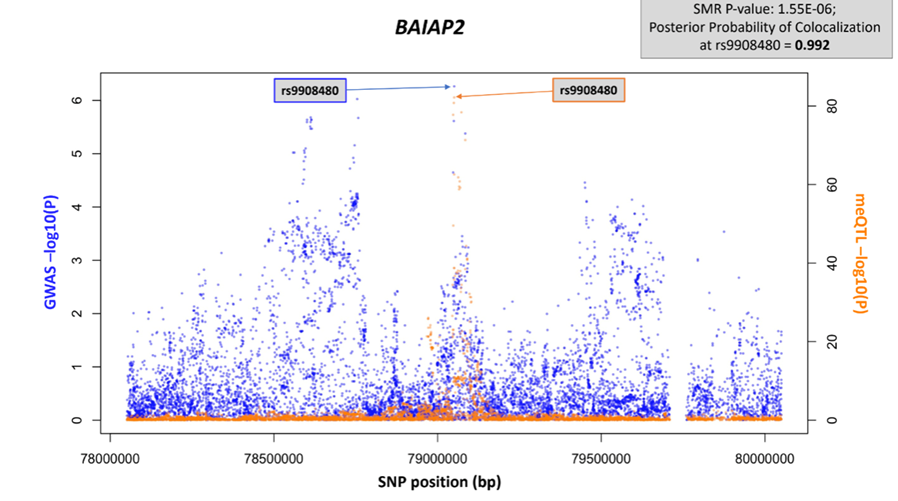
The researchers identified 420 CpG sites across 314 independent loci to be significantly associated with incident T2D. Fine-mapping also identified multiple additional CpG sites that were more strongly predictive of T2D than evaluation based on low-coverage microarray alone.

To find out more about how NSCC’s HPC resources can help you, please contact e-news@nscc.sg.
NSCC NewsBytes July 2024